1. What is vegetal chitosan?
Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed β-(1→4)-linked D-glucosamine (deacetylated unit) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (acetylated unit).
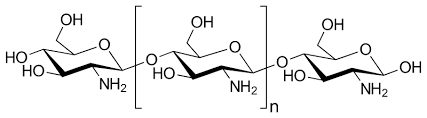
Chitosan, sometimes known as deacetylated chitin, is a natural polycationic linear polysaccharide derived from partial deacetylation of chitin. Chitin is the structural element in the exoskeleton of insects, crustaceans (mainly shrimps and crabs shell), and cell walls of fungi (oyster mushroom, agaricus bisprous and aspergillus niger), and also is the second most abundant natural polysaccharide after cellulose.

Chitosan, a natural polysaccharide prepared of fungal origin, is initially extracted and purified from reliable and abundant food or biotechnological fungal sources such as Agaricus bisporus or Aspergillus niger.
Chitosan is obtained by hydrolysis of a chitin-rich extract. Chitin is a polysaccharide composed of several N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units interconnected by ß→(1.4) type linkages.
Chitosan is composed of glucosamine sugar units (deacetylated units) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units (acetylated units) interconnected by ß→(1.4) type linkages.
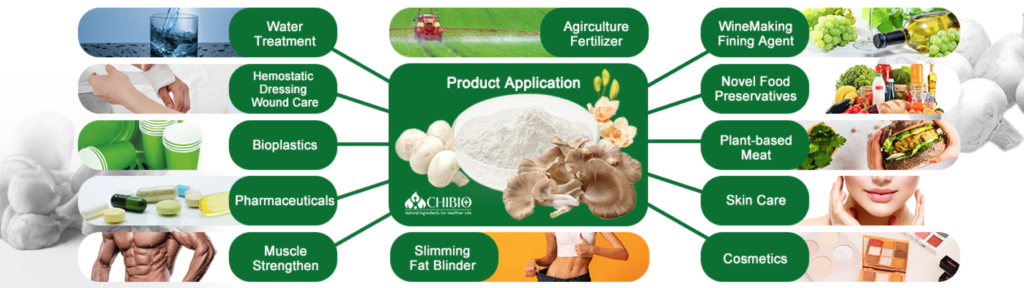
Chitosan has been widely used in various fields, including wine, pharmaceuticals, dietary supplement, medicine, agriculture, and food industries, due to its biocompatibility, biodegradability, and non-toxicity. In recent years, researchers have investigated the use of vegetal chitosan, which is derived from fungal or plant sources, as a sustainable alternative for use in wine applications.
2. What are the advantages of vegetal chitosan?
Vegetal chitosan, also known as fungal chitosan or mycelium chitosan, is a type of chitosan derived from the cell walls of fungi (mushroom and aspergillu niger). It has several advantages over traditional chitosan derived from shellfish, including:

- 1. Vegan and vegetarian-friendly: Vegetal chitosan is an excellent alternative for individuals who avoid animal-based products, such as those who follow a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle.
- 2. Allergen-free: Traditional chitosan is derived from shellfish, which can cause allergic reactions in some people. Vegetal chitosan does not contain any shellfish-derived ingredients, making it an allergen-free option.
- 3. Purer: Vegetal chitosan is often considered to be purer than traditional chitosan because it is derived from a single source, whereas traditional chitosan can be contaminated with other shellfish-related substances.
- 4. Better solubility: Vegetal chitosan is more soluble than traditional chitosan, which makes it easier to incorporate into various applications such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, wine and food.
- 5. Improved bioavailability: Some studies have suggested that vegetal chitosan has a higher bioavailability compared to traditional chitosan, which means that it can be absorbed and utilized more effectively by the body.
Overall, vegetal chitosan offers several advantages over traditional chitosan, making it an attractive alternative for individuals and industries looking for a vegan, allergen-free, and more effective chitosan source.
3. What are the benefits of vegetal chitosan in food application?
Vegetal chitosan represents a significant advancement in the field of biopolymers, emerging as a sustainable and effective alternative to traditional animal-derived chitosan. Extracted from the cell walls of fungi, vegetal chitosan offers unique properties that make it ideal for various applications, particularly in the food industry.
The unique structure and properties of vegetal chitosan contribute to its numerous benefits, including biodegradability, biocompatibility, and non-toxicity. Its ability to form films and gels makes it an excellent agent for enhancing the quality and shelf-life of various food products.
Vegetal chitosan, derived from fungal sources as an alternative to traditional animal-based chitosan, offers several benefits in food applications, including:
(1)Food Preservation and Shelf Life Extension: Vegetal chitosan has excellent antimicrobial properties, making it effective against a wide range of food spoilage organisms and pathogens. This helps in extending the shelf life of perishable food items like fruits, vegetables, and meats.

(2)Food Safety: By inhibiting the growth of harmful microorganisms, vegetal chitosan enhances the safety of food products. This is particularly significant in mitigating the risk of foodborne illnesses.
(3)Enhancement of Food Quality: It can be used to maintain or enhance the quality of food products. For instance, it can help in retaining moisture, preserving texture, and maintaining the nutritional value of foods.
(4)Food Coatings and Edible Films: Vegetal chitosan can form thin, biodegradable films that can be used as coatings for various food items. These films act as barriers to oxygen, moisture, and microbial contamination, further contributing to food preservation.

(5)Natural and Sustainable: Being derived from a vegetal source, it is an attractive alternative for those seeking sustainable and eco-friendly food processing aids. It aligns with the increasing consumer demand for natural and plant-based food additives.
(6)Food Processing Aid: It can be used as a flocculant in the clarification of beverages, like juices and wines, helping to remove unwanted particles and improve clarity and quality.

(7)Reducing Allergenicity and Enhancing Functional Properties: For products like plant-based meats or cultivated meat, vegetal chitosan can help in improving texture and binding ingredients together, while potentially reducing allergenicity compared to animal-based chitosan.

(8)Biodegradable Packaging Material: When used in packaging, vegetal chitosan-based materials offer an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional plastics, being biodegradable and often compostable.
(9)Control of Fat Absorption: In fried foods, coatings with chitosan can reduce the absorption of oil, leading to lower-calorie products.
(10)Regulatory Acceptance: With increasing scrutiny on food additives, vegetal chitosan, particularly because of its natural origin, might face fewer regulatory hurdles compared to synthetic additives.
These benefits make vegetal chitosan a highly versatile and valuable component in the food industry, contributing not only to the safety and quality of food products but also aligning with the growing trends towards sustainability and natural ingredients.
4. What is the dosage recommendation of vegetal chitosan in food?
Determining the optimal dosage of vegetal chitosan depends on the specific application and desired outcome. Generally, concentrations range from 0.5 to 2.0% (w/v), but specific applications may require tailored concentrations. Adherence to regulatory guidelines and safety assessments is crucial in determining the appropriate dosage.
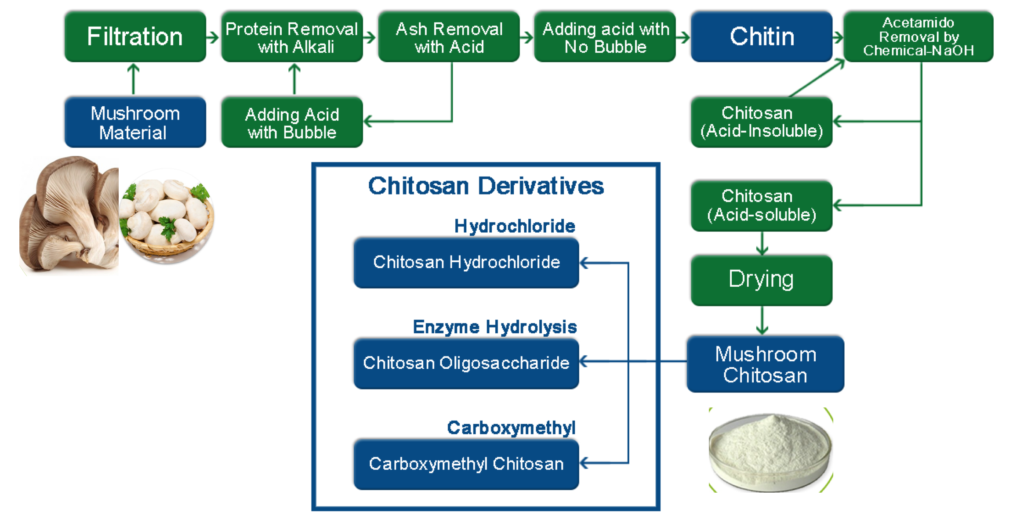
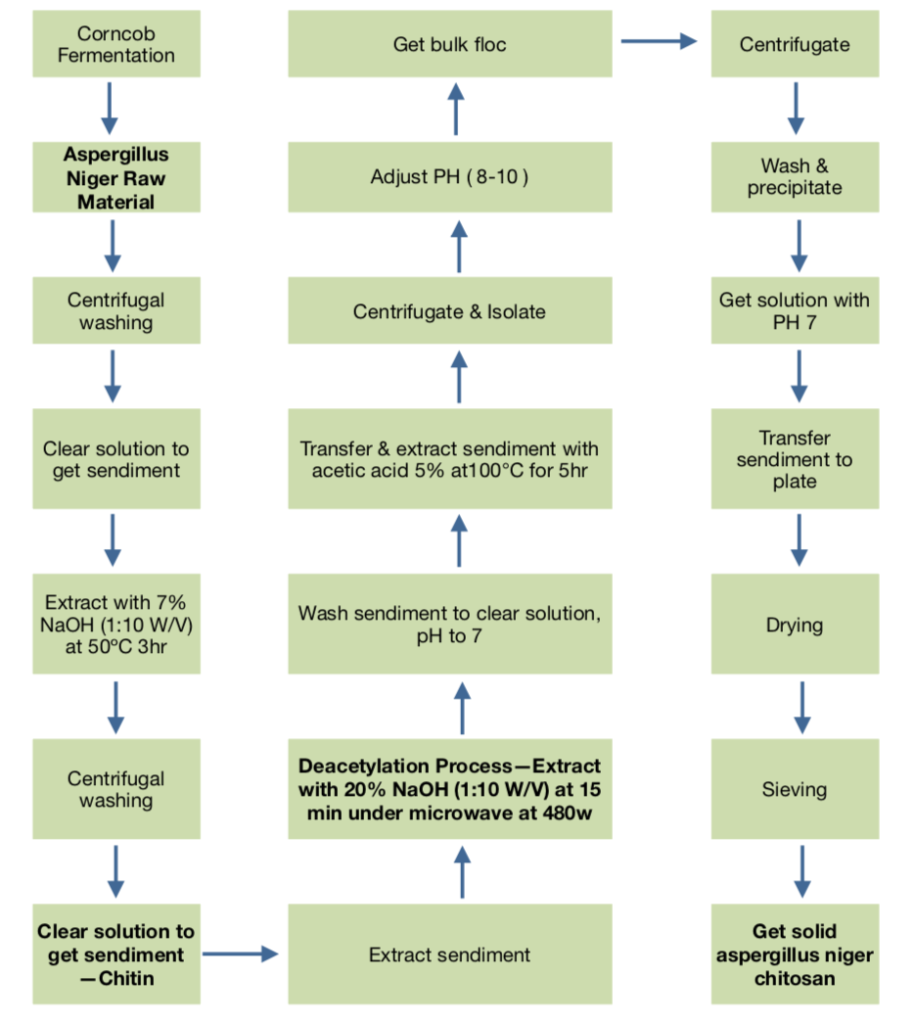
5. What is the flowchart of vegetal chitosan processing?
The production process of plant chitosan is mainly obtained by extracting raw materials (mushrooms, Aspergillus niger), deproteinizing with dilute acid or alkali, deacetylating, drying, etc.
Here is a simplified flowchart of the production process of vegetal chitosan for your reference.
6. In summary of vegetal chitosan in food application:
Vegetal chitosan is a versatile and sustainable biopolymer offering considerable benefits in the food industry. Its properties, including biodegradability, antimicrobial activity, and ability to form films, make it a valuable tool in food preservation, processing, and packaging. As the demand for environmentally friendly and safe food processing aids grows, vegetal chitosan stands out as a promising solution.

