. Chitosan
Used in Food, Cosmetics, Pharmaceuticals, Wine & over 23 Applications
Suitable for Everyone, Especially for Vegan, Vegetarian & Those with Shellfish-allergic
Vegetal / Fungal / Vegan Chitosan
Vegetal chitosan is a natural biopolymer derived from the cell walls of fungi, specifically mushrooms, aspergillus niger.
It is known for its antimicrobial, antioxidant, and biocompatible properties, making it useful in applications like food preservation, medical treatments, cosmetics, dietary supplement, agriculture and other various industries.
Source: Oyster Mushroom (Scientific Name: Pleurotus Ostreatus) & Agaricus Bisporus & Organic Mushroom
Types:
Acid-soluble Mushroom Chitosan
Water-soluble:
Mushroom Chitosan Hydrochloride
Mushroom Chitosan Oligosaccharide
Mushroom Carboxymethyl Chitosan
Source: Aspergillus Niger (Corn Cob Fermentation)
Types:
Acid-soluble Aspergillus Niger Chitosan
High Density Aspergillus Niger Chitosan
Water-soluble:
Aspergillus Niger Chitosan Hydrochloride
Aspergillus Niger Chitosan Oligosaccharide
100% Plant-based Natural Chitosan
- Source: Oyster mushroom (Scientific name: Pleurotus ostreatus)
- Certificate: USDA NOP, ECO CERT
Advantages & Benefits of Vegetal Chitosan
GMO-free
Allergen-free
Gluten-free
Toxicity-free
Curelty-free
Irradiation-free
Biodegradable
Biocompatible
Renewable
Food Grade
Antimicrobial & Antibacterial
Antioxidant
100% Plant-based
Vegan
Environmental Friendly
Production Flowchart of Vegetal Chitosan
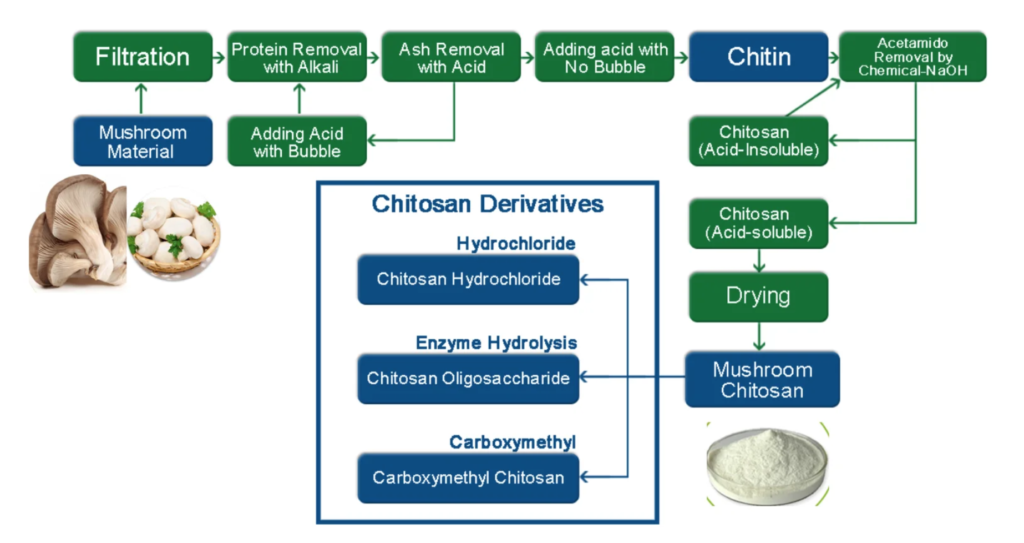
Flowchart of Mushroom Chitosan
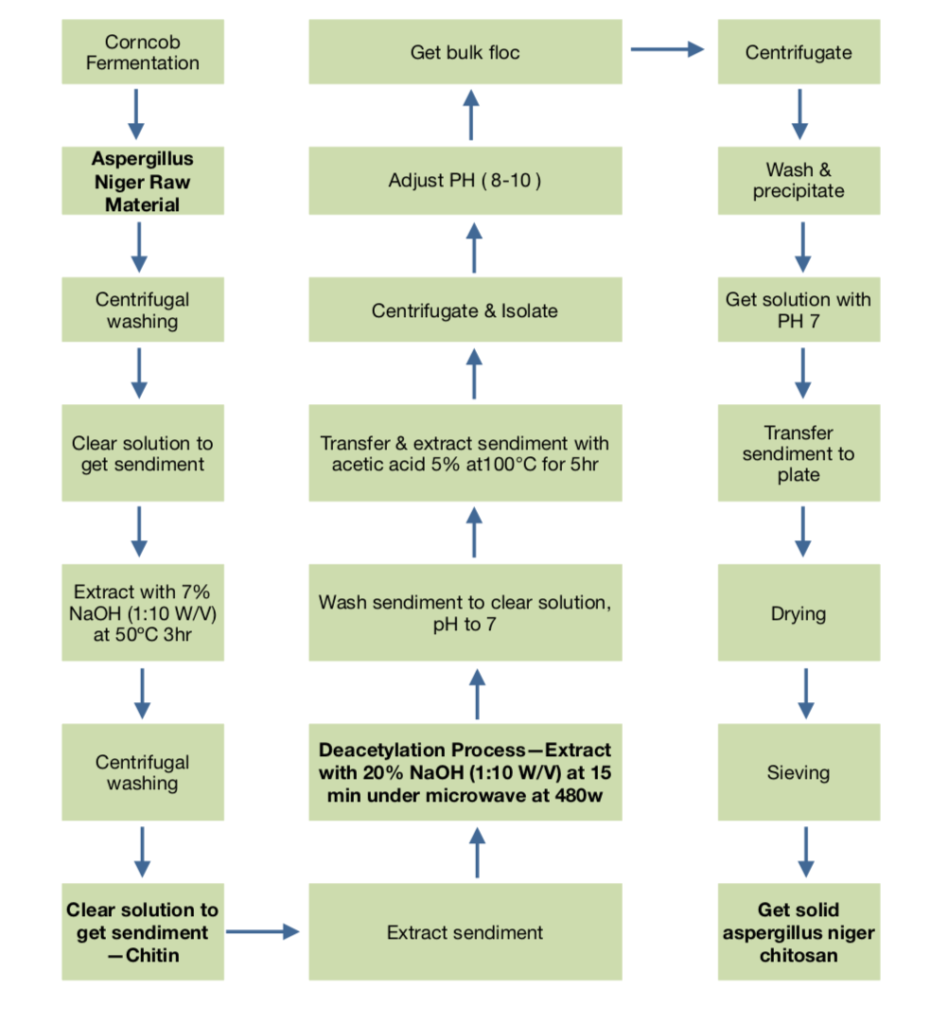
Flowchart of Aspergillus Niger Chitosan
Biotechnology Research & Product Development
Innovation distinguishes a leader from a follower.
As leaders in vegetal chitosan, Chibio Biotech are committed to researching and developing innovative natural ingredients to meet diverse industrial requirements.
High Deacetylation
85%~98%
Various Viscosity
20cps(mPa.s) ~ 1000cps(mPa.s)
Various Molecular Weight
20kDa~1500kDa
Solubility
Acid-soluble & Water-soluble
Derivatives
Hydrochloride, Oligosaccharide & Carboxymethyl (N/O/N,O-CMC)
Protein Removal
NMT 2%
Low Glucan
NMT 2%
Low Heavy Metal
As, Pb, Cd, Hg
Density
NLT 0.3~0.7g/cm3
Microbiological
Total Plat Count, Yeast & Mold, etc
Knowledge of Vegetal Chitosan
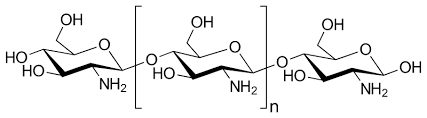

1. What is Chitosan?
Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed β-(1→4)-linked D-glucosamine (deacetylated units) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (acetylated units). It is a natural, biodegradable polymer derived from chitin, which is found in the exoskeletons of crustaceans such as shrimp, crabs, and lobsters, as well as in the cell walls of certain fungi like mushrooms (oyster mushroom & agaricus bisporus known as white button mushroom) and Aspergillus niger.
Chitosan is produced by deacetylating chitin, a process that involves treating it with an alkaline substance to remove acetyl groups. This results in a natural polycationic linear polysaccharide known for its versatility and numerous beneficial properties.
As a biomaterial, chitosan exhibits:
- Antibacterial Properties
- Antioxidant Properties
- Non-toxicity
- Low Allergenicity
- Biocompatibility
- Biodegradability
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies chitosan as “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS) (Casettari and Illum, 2014). It is the second most abundant natural polysaccharide after cellulose and finds applications across various industries due to its well-documented characteristics.
Chitosan History Timeline
Year 1811
Chitin Discovery
French chemist Henri Braconnot first discovered chitin in mushrooms.
Year 1859
Chitosan Transformation
French scientist Charles Rouget converted chitin to chitosan through alkali treatment for the first time.
Mid-20th Century
Marine Chitosan Maturation
The extraction process of chitosan from marine crustaceans (like shrimp and crabs) matured, becoming the primary commercial source, mainly used in medical, agricultural, and food additive fields.
Late 20th Century
Fungal Chitosan Exploration
With increasing demand, scientists started exploring plant and fungal sources of chitosan due to allergy concerns and environmental sustainability issues.
Year 1990s
Fungal Chitosan Achieved
Scientists developed methods to extract chitosan from various fungi (like mushrooms and Aspergillus niger), achieving initial success.
Early Year 2000s
Vegetal Chitosan Commercialization
Commercial production and sale of plant-based chitosan began. Biotechnology companies, such as Chibio Biotech, played a significant role in advancing production techniques and applications.
Year 2010s
Vegetal Chitosan Commercialization
Plant-based vegetal chitosan gained widespread recognition and adoption across multiple industries, including food additives, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture, wine, dietary supplement and other fields.
Today & Future
Sustainability
Plant-based vegetal chitosan holds an important market position due to its multifunctionality and benefits (e.g., antibacterial and antioxidant properties).
Production methods continue to improve, ensuring its sustainability and value in the market.
2. Why Do You Focus on Vegetal Chitosan?

Environmental Protection
Vegetal chitosan is more eco-friendly than crustacean chitosan, reducing reliance on marine resources and promoting sustainable practices.

Animal Protection
Using vegetal chitosan protects marine life by reducing the need to harvest shrimp, crabs, and lobsters, supporting animal welfare.

Allergy Concerns
Crustacean chitosan poses allergy risks and is unsuitable for vegans and vegetarians. With the growing vegan population and about 80 to 160 million people allergic to crustaceans, vegetal chitosan offers a safe alternative for food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals, etc.
With the growing demands for plant-based non-animal ingredients, Fungal Chitosan, sourced from mushroom (oyster mushroom, White Button Mushroom named as agaricus bisporus) and aspergillus niger, was becoming one of the most potential plant-sourced ingredient.
Thanks to its properties: antimicrobial, antioxidant, 100% biodegradable, biocompatibility, fungal chitosan was widely used in novel food preservatives, plant-based meat, winemaking fining agent, cosmetics ( skincare, haircare), fat binder, food supplement, wound dressing , pharmaceuticals, bioplastics, agriculture and other fields.
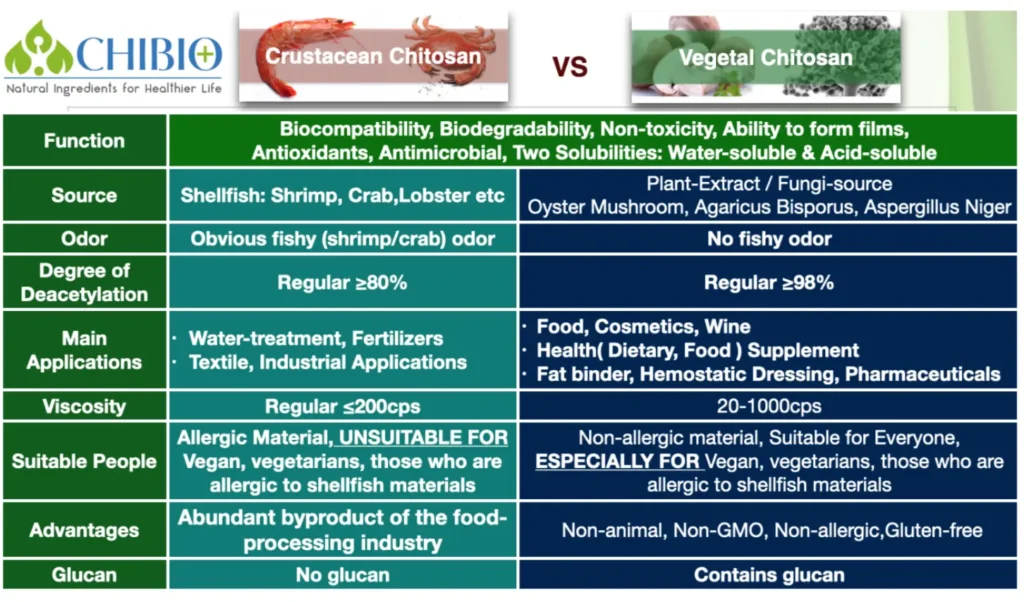
3. What is the Comparison between Crustacean Chitosan & Vegetal Chitosan?
Both crustacean and vegetal chitosan offer biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-toxicity, antioxidants, antimicrobial properties, film-forming abilities, and two types of solubility (water-soluble and acid-soluble).
However, crustacean chitosan, derived from shellfish, has a fishy odor and is unsuitable for vegans, vegetarians, and those with shellfish allergies.
In contrast, vegetal chitosan, derived from plants (mushroom) and fungi (aspergillus niger), is odorless, highly deacetylated, non-allergic, and suitable for a wider range of applications, including food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
4. Which Application Fields is Vegetal Chitosan Used For?
The unique characteristics of vegetal chitosan, such as biocompatibility, non-toxicity, Non-allergen, and biodegradability, antitumor, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activities make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Vegetal chitosan and its derivatives have seen significant development, as evidenced by the growing number of related publications over the years.
The applications listed below are for your reference, and more applications are continually being developed.
Vegetal chitosan can be used extensively in various fields, including:
- Food preservatives
- Winemaking as a fining agent
- Cosmetics
- Dietary Supplement
- Agriculture fertilizer
- Water treatment
- Wound-healing materials
- Pharmaceutical
- Weight Management
- Bio-packaging
Vegetal Chitosan
Effective for Over 23 Applications with Positive Feedback
10 Types of Vegetal Chitosan
Please select the corresponding type
according to your application field or specification requirements
| Item | Product Name | Main Applications |
|---|---|---|
| GBS001 | Acid Soluble Mushroom Chitosan 20-100cps | Dietary supplement,Food Preservatives |
| GBS002 | Acid Soluble Mushroom Chitosan 100-500cps | Pharmaceuticals, Bio-package, Biol-eather |
| GBS003 | Acid Soluble Mushroom Chitosan 500-1000cps | Flocculant Agent, Wound Care, Fragrance |
| GBS004 | Water Soluble Mushroom Chitosan Hydrochloride | Skincare, Cosmetics, Haircare |
| GBS005 | Water Soluble Mushroom Chitosan Oligosaccharide (NMT 5K Da) | Cosmetics, Agriculture, Medical Spray |
| GBS006 | Acid Soluble Aspergillus Niger Chitosan | Wine/Beverage Fining Agent |
| GBS007 | Water Soluble Aspergillus Niger Chitosan Hydrochloride | Cosmetic, Skincare, Haircare |
| GBS008 | Water soluble Aspergillus Niger Chitosan Oligosaccharide | Cosmetics, Agriculture, Medical Spray |
| GBS009 | High Density Aspergillus Niger Chitosan | Weight-loss Capsule/Tablet, Fat Binder |
| GBS010 | Water Soluble Mushroom Carboxymethyl Chitosan | Growth/Tissue Regeneration, Wound Healing Dressing, Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics |
Videos
Watch the videos of the solubility process of vegetal chitosan in acid or water for your applications.
Get in touch with us
Boost your application formulation by vegetal chitosan now!
Start using 100% plant-based vegetal chitosan in your applications!
Please contact us for free samples or additional information.
Our team is happy to answer your questions.





