1. What is vegetal chitosan?
Chitosan is a natural biopolymer that is primarily derived from chitin, which is the second most abundant natural polysaccharide after cellulose. Chitin is commonly found in the exoskeletons of crustaceans like crabs, shrimps, and lobsters, as well as in the cell walls of certain fungi like mushroom, aspergillus niger.
Structure and Properties:
- Chemical Structure: Chitosan is obtained by deacetylating chitin. This process involves removing acetyl groups from chitin, resulting in a polymer that has free amine groups.
- Solubility: Unlike chitin, chitosan is soluble in acidic to neutral solutions, making it more versatile for various applications.
- Biocompatibility and Biodegradability: Chitosan is known for its excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability. It’s non-toxic and can be broken down by natural biological processes.
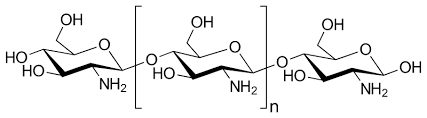
Chitosan, sometimes known as deacetylated chitin, is a natural polycationic linear polysaccharide derived from partial deacetylation of chitin. Chitin is the structural element in the exoskeleton of insects, crustaceans (mainly shrimps and crabs shell), and cell walls of fungi (oyster mushroom, agaricus bisprous and aspergillus niger), and also is the second most abundant natural polysaccharide after cellulose.

Chitosan, a natural polysaccharide prepared of fungal origin, is initially extracted and purified from reliable and abundant food or biotechnological fungal sources such as Agaricus bisporus or Aspergillus niger.
Chitosan is composed of glucosamine sugar units (deacetylated units) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units (acetylated units) interconnected by ß→(1.4) type linkages.
Uses and Applications:
- Medical and Pharmaceutical Fields: Due to its biocompatibility and non-toxic nature, chitosan is used in wound healing, drug delivery systems, and as a biomaterial in tissue engineering.
- Water Treatment: Its ability to bind with heavy metals and other contaminants makes it useful in water purification and treatment processes.
- Agriculture: As a natural biostimulant and elicitor, chitosan is used to enhance plant growth and provide resistance against pathogens.
- Food Industry: It’s used as a food additive for its antimicrobial properties, and as an edible film or coating to enhance the shelf life of perishable food products.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: In this realm, it finds use as a thickener, moisturizer, and film-forming agent, particularly in hair and skin care products.
Chitosan has been widely used in various fields, including wine, pharmaceuticals, dietary supplement, medicine, agriculture, and food industries, due to its biocompatibility, biodegradability, and non-toxicity. In recent years, researchers have investigated the use of vegetal chitosan, which is derived from fungal or plant sources, as a sustainable alternative for use in wine applications.
Variants:
- Traditional Chitosan: Traditionally sourced from marine crustaceans.
- Vegetal Chitosan: Derived from fungal sources, offering an alternative for those seeking non-animal derived products.
In summary, chitosan’s versatility, biodegradability, and non-toxic nature make it a valuable material across various industries, from healthcare to cosmetics. Its ability to be derived from non-animal sources also makes it an appealing option for vegetarian and vegan-friendly products.
2. What are the advantages of vegetal chitosan?
Vegetal chitosan, also known as fungal chitosan or mycelium chitosan, is a type of chitosan derived from the cell walls of fungi (mushroom and aspergillu niger). It has several advantages over traditional chitosan derived from shellfish, including:

- 1. Vegan and vegetarian-friendly: Vegetal chitosan is an excellent alternative for individuals who avoid animal-based products, such as those who follow a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle.
- 2. Allergen-free: Traditional chitosan is derived from shellfish, which can cause allergic reactions in some people. Vegetal chitosan does not contain any shellfish-derived ingredients, making it an allergen-free option.
- 3. Purer: Vegetal chitosan is often considered to be purer than traditional chitosan because it is derived from a single source, whereas traditional chitosan can be contaminated with other shellfish-related substances.
- 4. Better solubility: Vegetal chitosan is more soluble than traditional chitosan, which makes it easier to incorporate into various applications such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, wine and food.
- 5. Improved bioavailability: Some studies have suggested that vegetal chitosan has a higher bioavailability compared to traditional chitosan, which means that it can be absorbed and utilized more effectively by the body.
Overall, vegetal chitosan offers several advantages over traditional chitosan, making it an attractive alternative for individuals and industries looking for a vegan, allergen-free, and more effective chitosan source.
3. What are the benefits, functions of vegetal chitosan in weight-loss?
Vegetal chitosan, derived from fungal sources ( mushroom) or fermentation processes (aspergillus niger) as opposed to the traditional method from shellfish, offers several benefits and functions that make it a potentially useful aid in weight loss:
Benefits of Vegetal Chitosan in weight-loss
- Weight Loss Support: By preventing the absorption of a portion of ingested fats, chitosan can help reduce overall calorie intake, supporting weight loss efforts.

- Cholesterol Management: The reduction in absorbed fats leads to lower cholesterol levels, which is beneficial for cardiovascular health and can indirectly support weight management.

- Appetite Suppression: Although more indirectly and subject to individual variation, the presence of chitosan in the digestive system can increase satiety (the feeling of fullness) and potentially reduce overall calorie intake.

- Improved Digestive Health: As a form of dietary fiber, chitosan improves digestive health, which is essential for efficient metabolism and weight management.

Functions of Vegetal Chitosan in weight-loss
- Fat Binding: Vegetal chitosan binds to dietary lipids in the digestive tract, forming complexes with fats that are too large to be absorbed by the body. This leads to a direct reduction in the amount of fat absorbed.

- Blood Sugar Regulation: Chitosan interferes with the absorption of sugar in the intestine, helping to maintain more stable blood sugar levels, which can prevent high insulin spikes that promote fat storage.

- Toxin Binding: Chitosan has the capacity to bind to toxins and heavy metals in the digestive system, aiding in their excretion and thus reducing the body’s toxic load.

These functions and benefits show how vegetal chitosan can be an effective adjunct in a weight management plan, particularly when combined with lifestyle changes like diet and exercise.
4. What is the dosage or formula guideline of vegetal chitosan used in weight-loss?
The appropriate dosage of vegetal chitosan for weight loss can vary depending on several factors, including the specific formulation of the product, the purity of chitosan used, and individual health conditions. However, I can provide some general guidelines based on available research and typical usage:

- Standard Dosage: The common dosage of chitosan for weight loss purposes generally ranges from about 500 mg to 3,000 mg per day. This dosage is usually split into two or more doses, taken before meals to maximize its fat-binding capacity.
- Based on Meals: Some recommendations suggest taking chitosan just before meals with a full glass of water. This timing helps chitosan bind effectively to fats present in the meal.
- Duration: For weight loss, chitosan is often taken on a daily basis for periods ranging from a few weeks to several months. Continuous, long-term use should be monitored by a healthcare provider to assess effectiveness and safety.
- Considerations:
- It’s important to follow the dosage instructions provided on the product label or those given by a healthcare provider.
- Higher doses are sometimes used under medical supervision, especially in studies examining the effects of chitosan on cholesterol and other metabolic parameters.
- Safety and Side Effects: While generally considered safe, chitosan can cause gastrointestinal side effects such as constipation or gas. People with shellfish allergies should avoid chitosan derived from shellfish sources, although vegetal chitosan may be a viable alternative.
- Effectiveness: The effectiveness of chitosan can vary. Some studies show modest effects on weight loss and cholesterol levels, while others find no significant benefits. The variation in results suggests that outcomes may be influenced by individual differences in metabolism and diet.
For the most accurate and personalized advice, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional who can consider personal health status and specific needs. This ensures the supplementation is not only effective but also safe.
5. What is form of vegetal chitosan in weight-loss?
Vegetal chitosan for weight loss is available in various forms, each designed to suit different preferences and usage scenarios. Here are the common forms in which vegetal chitosan is typically found as following, along with specific guidelines that can help you choose and use the right form effectively::
- Capsules: One of the most common forms, capsules are convenient for controlling dosage and for those who prefer not to taste the supplement. They are easy to take, especially before meals, which is recommended for maximizing chitosan’s fat-binding effects.
- Dosage: Typically, dosages range from 500 mg to 3,000 mg per day, split across 2-3 doses, ideally taken before meals to maximize fat-binding effects.
- Instructions: Capsules should be taken with a full glass of water to aid in swallowing and to ensure that the chitosan reaches the stomach effectively.

- Tablets: Similar to capsules, tablets offer a convenient and dose-controlled way to take chitosan. They might include binders or fillers to maintain their shape but are generally just as effective as capsules.
- Dosage: Similar to capsules, the dosage for tablets is often between 500 mg and 3,000 mg daily, depending on the concentration of chitosan in each tablet.
- Instructions: Tablets are also best taken before meals with plenty of water to enhance the interaction of chitosan with dietary fats.

- Powder: Chitosan powder can be mixed into drinks, smoothies, or foods. This form allows for more flexibility in dosing and can be easier for those who have difficulty swallowing pills. However, measuring the dosage accurately is crucial.
- Dosage: The dosing for powder can vary more widely because it needs to be measured out. Careful adherence to packaging instructions for the equivalent of approximately 500 mg to 3,000 mg daily is recommended.
- Instructions: Mix the powder into a glass of water, juice, or a smoothie. Ensure it’s well-dissolved before consuming, and take it before meals for best results.

- Chewables: Less common but user-friendly, especially for those who might have difficulties with swallowing capsules or tablets. Chewables may be flavored to improve taste.
- Dosage: Dosages for chewable forms of chitosan should be specified on the product label, often aligned with the 500 mg to 3,000 mg range per day.
- Instructions: Chew the product thoroughly before swallowing. Taking chewables before meals can also help optimize fat-binding.

General Guidelines:
- Consistency: For any form of chitosan, consistency in timing relative to meals enhances effectiveness since chitosan works by interacting with fats in the stomach.
- Hydration: Adequate water intake with all forms of chitosan is important, as it helps transport the chitosan to the stomach and can aid in the digestion process.
- Health Considerations: Always check with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have allergies, are on medication, or have chronic health issues.
Each form of vegetal chitosan offers different conveniences, and has its own advantages in terms of ease of use, portability, and taste, so your choice might depend on your lifestyle, preferences for intake, and any specific dietary needs.
6. Which type of chitosan is best for weight-loss?
Choosing the best type of chitosan for weight loss depends on specific needs and health goals. Each type of chitosan—acid-soluble chitosan, chitosan hydrochloride, chitosan oligosaccharide, and carboxymethyl chitosan—offers distinct advantages that can contribute to weight management in different ways:
- Acid-Soluble Chitosan:
- Properties: This type of chitosan is soluble in acidic environments, such as the stomach. It is the traditional form of chitosan derived from shellfish, but it can also be produced from fungal sources for those with shellfish allergies.
- Benefits: Primarily effective at binding fats in the acidic environment of the stomach.
- Best For: Those focusing solely on reducing the absorption of dietary fats, which can lead to a direct reduction in caloric intake.
- Weight Loss Mechanism: Acid-soluble chitosan works primarily by binding to fats in the stomach before they are absorbed. The acidic environment of the stomach helps dissolve the chitosan, allowing it to interact with dietary fats.
- Considerations: While effective in binding fats, acid-soluble chitosan may not be as readily absorbed in the intestines due to its poor solubility in neutral or basic environments, which could limit some of its potential systemic benefits, such as cholesterol management.
- Chitosan Hydrochloride:
- Properties: This form is made by combining chitosan with hydrochloric acid, enhancing its solubility in water compared to traditional chitosan.
- Benefits: Soluble in water, which enhances its bioavailability and absorption, potentially making it more effective at interacting with lipids.
- Best For: Individuals looking for an effective fat binder that also has better solubility compared to traditional chitosan, improving overall efficacy.
- Chitosan Oligosaccharide:
- Properties: This is a depolymerized version of chitosan, consisting of shorter polymer chains, which enhances its solubility and bioavailability.
- Benefits: Features smaller molecule sizes, which may improve its digestibility and bioactivity. Known for its prebiotic properties, it can enhance gastrointestinal health and systemic metabolic functions.
- Best For: Those seeking comprehensive metabolic benefits beyond fat binding, including improved gut health and enhanced overall metabolic rates.
- Carboxymethyl Chitosan:
- Properties: This form is chemically modified to contain carboxymethyl groups, which improve water solubility significantly.
- Benefits: Highly soluble and also possesses moisture-retaining properties, which can be beneficial for overall health. It binds fats and is useful in lowering blood lipid levels.
- Best For: Individuals interested in broader metabolic improvements, particularly in lipid metabolism and detoxification, alongside traditional weight loss mechanisms.
Conclusion:
- For straightforward fat binding, acid-soluble chitosan and chitosan hydrochloride are excellent choices, with chitosan hydrochloride offering enhanced solubility.
- For those who value additional health benefits like improved gastrointestinal health and blood sugar regulation, chitosan oligosaccharide is the best choice due to its prebiotic properties and smaller molecule size.
- If the goal includes improving systemic health effects such as enhanced lipid metabolism, carboxymethyl chitosan would be ideal.
The selection ultimately depends on personal health goals, any existing dietary restrictions, and how well one’s body tolerates chitosan. Consulting with a healthcare provider can provide further guidance tailored to individual health profiles and dietary needs.
In addition, based on the years’ market feedbacks, acid-soluble chitosan is more commonly used in capsule form as a fat binder for weight loss in the market. This traditional form of chitosan is favored for several reasons:
- Effective Fat Binding: Acid-soluble chitosan is particularly effective at binding to fats in the acidic environment of the stomach, which makes it a popular choice for weight loss supplements aimed at reducing fat absorption.
- Ease of Use: Capsules are a preferred form because they are easy to consume, mask any unpleasant taste, and provide a convenient way to control dosages. This is particularly important for supplements like chitosan, where dosage accuracy is key to achieving the desired effects.
- Market Availability: Acid-soluble chitosan has been available for a longer time compared to other, more soluble forms of chitosan. Its effectiveness and safety profile are well-established, making it a go-to option for manufacturers of weight loss supplements.
- Consumer Preference: Many consumers prefer capsules because they are familiar, portable, and generally regarded as an easy form of supplementation. This consumer preference drives the prevalence of acid-soluble chitosan in capsule form in the market.
While acid-soluble chitosan is effective as a fat binder, it’s worth noting that other forms of chitosan, especially water-soluble types like chitosan hydrochloride, are gaining attention for their enhanced solubility and potentially broader range of biological effects. However, in terms of market dominance for the specific application of weight loss through fat binding, acid-soluble chitosan in capsule form remains highly popular.
7. What is the working mechanism of vegetal chitosan in weight-loss?
Vegetal chitosan works through several mechanisms to aid in weight loss, primarily by interacting with dietary fats and affecting metabolic processes. Here’s a detailed look at how vegetal chitosan functions:
- Fat Binding: The primary mechanism through which vegetal chitosan aids in weight loss is by binding to fats in the stomach. Chitosan is a positively charged polymer, and since fats (lipids) are negatively charged at stomach pH levels, chitosan can effectively bind to them. This binding creates large complexes of fat and chitosan that the body cannot absorb. As a result, these complexes are excreted rather than digested, leading to a reduction in the total caloric intake from fats.
- Reduction of Fat Absorption: By binding with dietary fats, vegetal chitosan reduces the amount of fat absorbed by the intestines. Less fat absorption can contribute to a caloric deficit, which is essential for weight loss.
- Appetite Suppression: There is evidence to suggest that chitosan might help reduce appetite. This effect could be due to the increase in the viscosity of stomach contents after chitosan binds to fats, which may slow digestion and extend feelings of fullness. This delayed gastric emptying can lead to reduced overall food intake.
- Potential Impact on Cholesterol: Chitosan is also known to bind to bile acids or cholesterol, which might help lower blood cholesterol levels. Lower cholesterol can contribute to overall better health and support metabolic processes that are conducive to weight loss.
- Improved Gastrointestinal Health: As a form of dietary fiber, chitosan can help improve gastrointestinal function. A healthy digestive system is crucial for effective metabolism and can assist in weight management by improving nutrient absorption and maintaining regular bowel movements.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Some studies indicate that chitosan might help stabilize blood sugar levels by reducing the absorption rate of sugars in the intestine. Stable blood sugar levels can help prevent insulin spikes that lead to fat storage, thus supporting weight loss efforts.
These diverse mechanisms make vegetal chitosan a multi-functional agent in weight loss supplements, capable of affecting both the intake and digestion of dietary fats, as well as influencing overall metabolic health.
8. Is chitosan Effective and safe gene-based delivery of GLP-1 that is current very popular medicine for obesity?
Based on the study research: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21412280/, it focuses on the development and characterization of a chitosan-based nanoparticle for the delivery of GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) gene therapy. GLP-1 is a hormone involved in glucose regulation and appetite control, making it a promising target for treating obesity. This research explores the potential of chitosan as a carrier for gene therapy aimed at enhancing the body’s production of GLP-1, which could theoretically aid in weight loss and improve glucose homeostasis.
Effectiveness of Chitosan in Gene Delivery:
Chitosan’s natural properties make it an attractive candidate for gene delivery systems:
- Biocompatibility: Chitosan is biocompatible, meaning it’s generally safe to use within the body and does not typically provoke an immune response.
- Biodegradability: It breaks down into natural components in the body, reducing long-term toxicity risks.
- Enhanced Delivery: Its positive charge allows it to form stable complexes with negatively charged molecules like DNA or RNA, which can be beneficial for delivering genetic material into cells.
The specific study on the chitosan-based delivery system for the GLP-1 gene shows that this approach could potentially enhance the therapeutic effects of GLP-1, such as improved blood glucose control and reduced appetite, both key components in managing obesity.
Safety of Chitosan in Gene Delivery:
While chitosan is generally considered safe and has been used in various biomedical applications, the safety of a chitosan-based gene delivery system specifically for delivering the GLP-1 gene would need thorough evaluation in clinical trials. Here are a few considerations:
- Immunogenicity and Inflammatory Response: While chitosan is typically biocompatible, any gene therapy application needs to monitor for potential immune reactions or inflammation.
- Long-term Effects: The long-term effects of gene therapy, including potential off-target effects and the stability of gene expression, would need careful study.
- Regulation and Approval: Any gene therapy approach, particularly for treating common conditions like obesity, would require rigorous clinical testing and regulatory approval to confirm its efficacy and safety.
Conclusion:
Based on the properties of chitosan and the preliminary research into its use for GLP-1 gene delivery, there is potential for this approach in treating obesity. However, whether this is effective and safe for widespread clinical use will depend on the outcomes of detailed clinical trials designed to rigorously evaluate its therapeutic benefits and potential risks. The concept is promising, but more research is necessary to move from experimental stages to practical medical applications.
9. In summary of vegetal chitosan in weight-loss
Vegetal chitosan, derived from sources like mushrooms and Aspergillus niger, offers a multifaceted approach to weight loss. Its primary function is fat binding, where it interacts with dietary fats in the stomach to form large complexes that the body cannot absorb, effectively reducing the total caloric intake from fats.
This mechanism not only aids in direct weight loss but also helps in managing blood cholesterol levels, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.

Additionally, vegetal chitosan may enhance feelings of fullness and slow down digestion, which can lead to a decrease in overall calorie consumption by suppressing appetite.
Furthermore, vegetal chitosan has been shown to improve gastrointestinal health due to its fiber-like properties, which can promote regularity and improve nutrient absorption. It may also assist in stabilizing blood sugar levels, which helps in managing insulin response and preventing sudden spikes in hunger.
The diverse functionalities of vegetal chitosan, including its ability to bind toxins and potentially lower cholesterol, make it a versatile and beneficial supplement for those looking to manage their weight effectively. Its natural origin and the absence of significant side effects commonly associated with synthetic drugs further enhance its appeal as a weight management aid.

