1. What is vegetal chitosan?
Chitosan is a natural biopolymer that is primarily derived from chitin, which is the second most abundant natural polysaccharide after cellulose. Chitin is commonly found in the exoskeletons of crustaceans like crabs, shrimps, and lobsters, as well as in the cell walls of certain fungi like mushroom, aspergillus niger.
Structure and Properties:
- Chemical Structure: Chitosan is obtained by deacetylating chitin. This process involves removing acetyl groups from chitin, resulting in a polymer that has free amine groups.
- Solubility: Unlike chitin, chitosan is soluble in acidic to neutral solutions, making it more versatile for various applications.
- Biocompatibility and Biodegradability: Chitosan is known for its excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability. It’s non-toxic and can be broken down by natural biological processes.
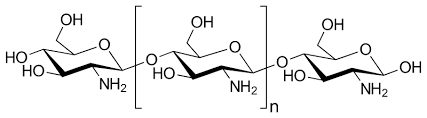
Chitosan, sometimes known as deacetylated chitin, is a natural polycationic linear polysaccharide derived from partial deacetylation of chitin. Chitin is the structural element in the exoskeleton of insects, crustaceans (mainly shrimps and crabs shell), and cell walls of fungi (oyster mushroom, agaricus bisprous and aspergillus niger), and also is the second most abundant natural polysaccharide after cellulose.

Chitosan, a natural polysaccharide prepared of fungal origin, is initially extracted and purified from reliable and abundant food or biotechnological fungal sources such as Agaricus bisporus or Aspergillus niger.
Chitosan is composed of glucosamine sugar units (deacetylated units) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units (acetylated units) interconnected by ß→(1.4) type linkages.
Uses and Applications:
- Medical and Pharmaceutical Fields: Due to its biocompatibility and non-toxic nature, chitosan is used in wound healing, drug delivery systems, and as a biomaterial in tissue engineering.
- Water Treatment: Its ability to bind with heavy metals and other contaminants makes it useful in water purification and treatment processes.
- Agriculture: As a natural biostimulant and elicitor, chitosan is used to enhance plant growth and provide resistance against pathogens.
- Food Industry: It’s used as a food additive for its antimicrobial properties, and as an edible film or coating to enhance the shelf life of perishable food products.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: In this realm, it finds use as a thickener, moisturizer, and film-forming agent, particularly in hair and skin care products.
Chitosan has been widely used in various fields, including wine, pharmaceuticals, dietary supplement, medicine, agriculture, and food industries, due to its biocompatibility, biodegradability, and non-toxicity. In recent years, researchers have investigated the use of vegetal chitosan, which is derived from fungal or plant sources, as a sustainable alternative for use in wine applications.
Variants:
- Traditional Chitosan: Traditionally sourced from marine crustaceans.
- Vegetal Chitosan: Derived from fungal sources, offering an alternative for those seeking non-animal derived products.
In summary, chitosan’s versatility, biodegradability, and non-toxic nature make it a valuable material across various industries, from healthcare to cosmetics. Its ability to be derived from non-animal sources also makes it an appealing option for vegetarian and vegan-friendly products.
2. What are the advantages of vegetal chitosan?
Vegetal chitosan, also known as fungal chitosan or mycelium chitosan, is a type of chitosan derived from the cell walls of fungi (mushroom and aspergillu niger). It has several advantages over traditional chitosan derived from shellfish, including:

- 1. Vegan and vegetarian-friendly: Vegetal chitosan is an excellent alternative for individuals who avoid animal-based products, such as those who follow a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle.
- 2. Allergen-free: Traditional chitosan is derived from shellfish, which can cause allergic reactions in some people. Vegetal chitosan does not contain any shellfish-derived ingredients, making it an allergen-free option.
- 3. Purer: Vegetal chitosan is often considered to be purer than traditional chitosan because it is derived from a single source, whereas traditional chitosan can be contaminated with other shellfish-related substances.
- 4. Better solubility: Vegetal chitosan is more soluble than traditional chitosan, which makes it easier to incorporate into various applications such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, wine and food.
- 5. Improved bioavailability: Some studies have suggested that vegetal chitosan has a higher bioavailability compared to traditional chitosan, which means that it can be absorbed and utilized more effectively by the body.
Overall, vegetal chitosan offers several advantages over traditional chitosan, making it an attractive alternative for individuals and industries looking for a vegan, allergen-free, and more effective chitosan source.
3. What are the benefits, functions of vegetal chitosan in bio-leather?
Vegetal chitosan, an innovative derivative of chitin sourced from non-animal origins: mushroom or fungi like aspergillus niger, is revolutionizing the production of bio-leather through its impressive array of benefits and functional advantages. This breakthrough material combines eco-friendliness with advanced performance features, making it an ideal choice for sustainable manufacturing. Here’s a detailed overview of its key benefits and functions:
Benefits of Vegetal Chitosan in Bio-Leather:
- Eco-Conscious Material Choice: Derived from sustainable sources like mushrooms and Aspergillus niger, vegetal chitosan is a testament to the commitment towards environmentally responsible materials. Its biodegradability ensures that products contribute minimally to pollution and waste, making it a cornerstone for green manufacturing practices.

- Reduced Environmental Impact: The use of vegetal chitosan eliminates the reliance on toxic chemicals typically associated with the tanning and finishing of traditional leathers. This shift not only safeguards ecosystems but also protects the health of those involved in the manufacturing process.

- Consumer Safety: With its natural origin, vegetal chitosan is allergy-free, making bio-leather products suitable for consumers who are sensitive to the allergens often present in synthetic materials. This feature is particularly appealing in the context of an increasingly health-conscious market.

Functions of Vegetal Chitosan in Bio-Leather:
- Structural Enhancement: Incorporating vegetal chitosan into bio-leather significantly improves its physical robustness. The material becomes more resistant to wear and tear, ensuring longevity and durability in everyday use—a crucial selling point for high-quality leather goods.

- Antimicrobial Activity: The inherent antimicrobial properties of chitosan contribute to a longer lifespan for bio-leather products by preventing microbial degradation and odor. This natural resistance makes chitosan-enhanced bio-leather ideal for applications where hygiene and freshness are paramount.

- Moisture Management: Vegetal chitosan enhances the water-resistance of bio-leather, protecting against moisture-induced damage. This function is vital for maintaining the structural integrity and aesthetic quality of leather goods, expanding their usability across different climates and conditions.

- Versatile Application: Thanks to its adaptable qualities, vegetal chitosan can be tailored for use in a variety of bio-leather products, ranging from high-fashion items to durable upholstery. This versatility opens up new avenues for designers and manufacturers to explore sustainable luxury.

By harnessing the natural efficacy of vegetal chitosan sourced from mushrooms and Aspergillus niger, bio-leather emerges not only as a viable alternative to traditional leathers but as a superior choice that aligns with both environmental ethics and consumer demands for sustainability and performance.
4. What are the common forms of vegetal chitosan in bio-leather?
In the production of bio-leather, vegetal chitosan, particularly when sourced from mushrooms and fungi like Aspergillus niger, can be utilized in several common forms to enhance the properties and functionality of the finished material:
- Chitosan Powder: This is the most straightforward form of vegetal chitosan used in bio-leather production. The powder can be dissolved in a solvent and then applied to the bio-leather substrate. This application can help in the cross-linking of fibers, improving durability, and imparting antimicrobial properties.
- Dosage: Typically, chitosan powder concentration ranges from 1% to 5% by weight relative to the material it’s being applied to.
- Application: The powder is often dissolved in a mild acidic solution (like acetic acid) to ensure it fully dissolves before application. It can then be applied through spraying or immersion methods during the tanning or post-tanning stages.

- Chitosan Solution: Vegetal chitosan powder can be dissolved in aqueous or organic solvents to form a chitosan solution. This solution can be used in the tanning process or as a finishing spray on bio-leather to enhance its mechanical properties, water resistance, and to provide an antimicrobial surface.
- Dosage: Concentrations in a solution can vary between 0.5% to 3%. The precise concentration depends on the desired strength and thickness of the bio-leather.
- Application: Applied through dipping, spraying, or padding. The pH of the solution should be adjusted (usually between 4.0 and 6.0) to ensure stability and effectiveness of the chitosan.

- Chitosan Films and Coatings: Chitosan can be processed into thin films and coatings that can be directly applied onto the surface of bio-leather. These films can provide a protective barrier against moisture, microbial growth, and physical abrasion.
- Dosage: Film thickness can vary but is generally in the range of a few microns to about 100 microns. The concentration of chitosan in the coating solution might be higher, typically around 1% to 2%.
- Application: The film or coating can be applied by brushing, spraying, or using a curtain coating technique to ensure an even layer.

- Chitosan Nanoparticles: For a more targeted and efficient application, chitosan can be engineered into nanoparticles. These nanoparticles can deeply penetrate the bio-leather, offering improved performance in terms of strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors.
- Dosage: Due to their high efficiency and surface area, lower concentrations such as 0.1% to 1% can be effective.
- Application: These can be incorporated into bio-leather via spraying or immersion methods, where they can penetrate deeply and distribute uniformly throughout the material.

- Chitosan Fibers: Although less common, chitosan can also be spun into fibers that can be woven or integrated into the structure of bio-leather, reinforcing the material from within or providing a unique texture to the surface.
- Dosage: Not precisely defined as it depends on the desired properties of the end product. Chitosan fibers can be blended with other fibers at various ratios depending on the application.
- Application: These fibers can be woven into the fabric or used as a non-woven mat that forms part of the bio-leather structure.

Each form of vegetal chitosan offers unique benefits and can be chosen based on the specific requirements of the bio-leather being produced, such as the desired physical properties, application methods, and environmental considerations.
For each application, the processing conditions such as temperature, pH, and time are critical and must be optimized based on the specific type of bio-leather and the desired properties. Experimentation and testing are essential to determine the optimal conditions for each specific case. Additionally, it’s important to ensure that all components used are compatible with vegetal chitosan to maintain the integrity and performance of the bio-leather.
5.Considering solubility, which type of chitosan is optimal for different bio-leather applications?
Considering solubility, the optimal type of chitosan for various bio-leather applications can vary among acid-soluble chitosan, chitosan hydrochloride, chitosan oligosaccharide, and carboxymethyl chitosan. Here’s a focused analysis to help determine the best fit:
- Acid-Soluble Chitosan: This type is highly soluble in acidic conditions, making it suitable for applications where pH adjustment is feasible and a stronger chitosan interaction with the material is desired.
- Application Area: Tanning and Retanning Processes
- Usage: This type of chitosan is ideal for use in the tanning stages where acidic conditions are common. It helps in enhancing the binding of the chitosan to the collagen fibers in the leather, improving the leather’s durability and resistance to physical wear.
- Chitosan Hydrochloride: Known for its excellent water solubility, chitosan hydrochloride is ideal for straightforward, aqueous processing environments, offering ease of use in diverse manufacturing settings.
- Application Area: Antimicrobial and Antifungal Treatments
- Usage: Due to its excellent solubility in water, chitosan hydrochloride is perfect for applications that require easy application and fast action, such as providing antimicrobial and antifungal properties to the bio-leather. This can be particularly useful in products like shoes and clothing where hygiene is paramount.
- Chitosan Oligosaccharide: With its low molecular weight, this variant is exceptionally soluble in water at various pH levels, ideal for lightweight finishing and treatments that require rapid absorption and minimal viscosity.
- Application Area: Leather Finishing
- Usage: The high solubility and low viscosity of chitosan oligosaccharide make it suitable for finishing treatments on bio-leather. It can be used in sprays or finishing baths to impart a soft touch, enhance color, and provide a protective barrier against moisture and stains.
- Carboxymethyl Chitosan: Outstanding in terms of solubility across all pH levels, carboxymethyl chitosan is highly versatile for a broad range of applications, particularly where variable pH environments and robust material integration are key.
- Application Area: Waterproofing and Moisture Barrier Coatings
- Usage: Carboxymethyl chitosan’s excellent solubility and adaptable viscosity make it an excellent choice for creating waterproof and protective coatings on bio-leather. It can be used to enhance the leather’s resistance to water and other liquids, making it ideal for outdoor apparel, footwear, and luxury leather goods that require extra protection against the elements.
Each type of chitosan brings unique properties to bio-leather applications, with the choice depending on specific process requirements and desired leather characteristics.
These specific applications take full advantage of the unique properties of each type of chitosan, ensuring that the bio-leather products are not only sustainable but also high in quality and functional in diverse environments.
6.Considering viscosity, which type of acid-soluble chitosan is optimal for different bio-leather applications?
When choosing the optimal type of acid-soluble chitosan for bio-leather applications based on different viscosity ranges (20-100 cps, 100-500 cps, 500-1000 cps), it’s important to consider how the viscosity affects the processing and final properties of the bio-leather. Here’s how different viscosities can be suited for specific applications:
- Low Viscosity (20-100 cps):
- Ideal Application: Finishing and Softening Treatments
- Explanation: Lower viscosity chitosan is excellent for finishing treatments where a lighter, more fluid application is required. It can easily penetrate the bio-leather, enhancing softness and flexibility without significantly altering the bulk properties or feel of the leather.
- Medium Viscosity (100-500 cps):
- Ideal Application: Intermediate Coatings and Moisture Barriers
- Explanation: This viscosity range is suitable for applications that require a more substantial coating, yet still need good penetration into the leather. It’s ideal for intermediate treatments that provide additional moisture resistance or act as a primer for further finishing layers. This range helps to improve durability and maintain the natural look and feel of the leather.
- High Viscosity (500-1000 cps):
- Ideal Application: Structural Enhancements and Protective Top Coats
- Explanation: Higher viscosity chitosan is beneficial for creating protective top coats or for use in treatments that require a thicker layer, which contributes to the overall structural integrity of the leather. These applications are critical in areas requiring enhanced wear resistance, such as in the production of footwear or high-traffic upholstery.
Each viscosity level of acid-soluble chitosan caters to a different phase of the leather treatment process, from deep penetration and softening to providing robust protective layers. Adjusting the molecular weight of the chitosan and its concentration in the treatment solutions can control the viscosity, thus allowing for precise application tailored to the needs of the bio-leather product.
7. Summarizing the vegetal chitosan benefits in bio-leather
Vegetal chitosan, derived from sustainable sources like mushrooms and Aspergillus niger, stands out as a revolutionary ingredient in the bio-leather industry, enhancing both the environmental appeal and functional superiority of leather products.
With its exceptional biodegradability, vegetal chitosan not only supports eco-friendly manufacturing practices but also significantly reduces the reliance on harmful chemicals typically associated with leather production.

This shift promotes a healthier ecosystem and safer working conditions, aligning perfectly with the growing global demand for sustainable consumer products.
In terms of functionality, vegetal chitosan elevates bio-leather by improving durability, resistance to wear and tear, and antimicrobial properties, thereby extending the lifespan and freshness of the leather goods.
Its versatility allows it to be applied in various forms—from powders and solutions to coatings and nanoparticles—each tailored to enhance specific characteristics of the bio-leather such as moisture resistance, structural integrity, and aesthetic finish.
Thus, vegetal chitosan is not merely an additive; it is a transformative agent that redefines the quality and sustainability of leather products in the contemporary market.

